Last update:
Molecular & Computational biology news

Team reports on relationship between contents of diosgenin and brassinosteroids in Dioscorea zingiberensis
Diosgenin, a secondary metabolite isolated from the Dioscorea spp. plant family, is an irreplaceable and ideal starting material for the synthesis of steroid hormone drugs. Dioscorea zingiberensis is the world's most desirable ...
Plants & Animals
7 hours ago
0
1

Unveiling the genetic blueprint of safflower
A research team has completed a high-quality chromosome-scale assembly of the Chuanhonghua 1 safflower genome. This work sheds light on the genetic underpinnings of crucial traits like linoleic acid (LA) and hydroxysafflor ...
Molecular & Computational biology
7 hours ago
0
15

SlTHM27-SlGAD2 model regulates the cold tolerance in tomato by regulating GABA and anthocyanin
The frequency and intensity of plant stresses have increased in recent years due to climate change. Among them, low temperature is an unavoidable environmental factor limiting agricultural productivity.
Molecular & Computational biology
7 hours ago
0
1

First chromosome-level reference genomes of the ornamental banana and pink banana
The genus Musa, encompassing approximately 70 herbaceous species, is predominantly found in the tropical and subtropical regions of Asia and Oceania. This genus is renowned for being one of the most important food crops globally ...
Molecular & Computational biology
7 hours ago
0
1

Researchers discover mechanism regulating bud dormancy release in tree peony
In perennial woody plants, bud endodormancy is crucial for survival under adverse environmental conditions in winter, such as low temperature (LT) and dehydration stress. To break bud dormancy is essential for the resumption ...
Molecular & Computational biology
7 hours ago
0
1

Mechanism of grafting Prunus sp. to control crown gall disease by regulating the rhizosphere environment
Grafting is a traditional and significant strategy to suppress soil-borne diseases, such as the crown gall disease caused by tumorigenic Agrobacterium and Rhizobium. Root exudates and the rhizosphere microbiome play critical ...
Molecular & Computational biology
7 hours ago
0
1

Enhancing sweet potato quality analysis with hyperspectral imaging and AI
Sweet potatoes are a popular food choice for consumers worldwide because of their delicious taste and nutritious quality. The red, tuberous root vegetable can be processed into chips and fries, and it has a range of industrial ...
Molecular & Computational biology
7 hours ago
0
1

Scientists map soil RNA to fungal genomes to understand forest ecosystems
If a tree falls in the forest—whether or not anyone registers the sound—one thing is for sure: there are lots of fungi around. Within a forest's soil, hundreds of species decompose debris, mobilize nutrients from that ...
Ecology
9 hours ago
0
106

Study suggests that cells possess a hidden communication system
Cells constantly navigate a dynamic environment, facing ever-changing conditions and challenges. But how do cells swiftly adapt to these environmental fluctuations?
Cell & Microbiology
9 hours ago
0
102

Researchers uncover 'parallel universe' in tomato genetics
In a paper appearing in Science Advances, Michigan State University researchers have unraveled a surprising genetic mystery centered on sugars found in what gardeners know as "tomato tar."
Molecular & Computational biology
10 hours ago
0
42

Can climate change accelerate transmission of malaria? New research sheds light on impacts of temperature
Malaria is a mosquito-borne disease caused by a parasite that spreads from bites of infected female Anopheles mosquitoes. If left untreated in humans, malaria can cause severe symptoms, health complications and even death.
Ecology
10 hours ago
1
36

International study produces a comprehensive 'tree of life' for flowering plants
With their own botanical collection material and their research knowledge on the evolution of cruciferous plants (plants of the cabbage family), bioscientists at Heidelberg University have contributed to a large-scale international ...
Plants & Animals
11 hours ago
0
7

Testing how well biomarkers work: New fluorescence microscopy method can improve resolution down to the Ångström scale
LMU researchers have developed a method to determine how reliably target proteins can be labeled using super-resolution fluorescence microscopy.
Molecular & Computational biology
11 hours ago
0
22

New method makes finding bat roosts easier for conservationists
A new algorithm is making it easier for ecologists and conservationists to find bat roost locations—reducing search areas by nearly 375 times their previous size. The technology combines microphone detector data with a ...
Ecology
12 hours ago
0
10
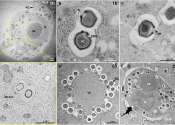
Giant virus discovered in wastewater treatment plant infects deadly parasite
The single-celled organism Naegleria fowleri ranks among the deadliest human parasites. Researchers around Matthias Horn and Patrick Arthofer from the Center for Microbiology and Environmental Systems Science at the University ...
Cell & Microbiology
12 hours ago
0
15

Biomolecular condensates: Study reveals poor predictive power of established liquid-liquid phase separation assays
Cells buzz with millions of different biomolecules that diffuse chaotically through their substructures, yet they manage to ensure exquisite functional and spatial specificity.
Cell & Microbiology
13 hours ago
0
11

Vast DNA tree of life for plants revealed by global science team using 1.8 billion letters of genetic code
A new paper published today (April 24) in the journal Nature by an international team of 279 scientists led by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew presents the most up-to-date understanding of the flowering plant tree of life.
Plants & Animals
13 hours ago
0
16

A key gene helps explain how the ability to glide has emerged over-and-over during marsupial evolution
People say "When pigs fly" to describe the impossible. But even if most mammals are landlubbers, the ability to glide or fly has evolved again and again during mammalian evolution, in species ranging from bats to flying squirrels. ...
Evolution
13 hours ago
0
1

Unveiling the mysteries of cell division in embryos with timelapse photography
The beginning of life is shrouded in mystery. While the intricate dynamics of mitosis are well-studied in the so-called somatic cells—the cells that have a specialized function, like skin and muscle cells—they remain ...
Cell & Microbiology
13 hours ago
0
14

Researchers unveil PI3K enzyme's dual accelerator and brake mechanisms
A group of researchers have expanded conventional knowledge on a critical enzyme that controls cell migration. In a publication in the journal Nature Communications, they reported that phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) not ...
Cell & Microbiology
13 hours ago
0
32
More news

World's chocolate supply threatened by devastating virus
New small molecule helps scientists study regeneration

A universal framework for spatial biology
Researchers uncover natural variation in wild emmer wheat for broad-spectrum disease resistance
Scientists reveal new path to increasing lactation for nursing mothers

Supercomputer simulation reveals new mechanism for membrane fusion

Using bacteriophage-derived lysin to target odor-causing bacteria in armpits
Liquid droplets shape how cells respond to change, shows study
Pressure in the womb may influence facial development

A small factor makes a big impact on genome editing
The enemy within: How pathogens spread unrecognized in the body
Researchers map protein network dynamics during cell division
Other news

Lunar landforms indicate geologically recent seismic activity on the moon

Researchers show it's possible to teach old magnetic cilia new tricks

Imaging technique shows new details of peptide structures

These giant, prehistoric salmon had tusk-like teeth

How evolution has optimized the magnetic sensor in birds
New method could cut waste from drug production

A shade closer to more efficient organic photovoltaics
Scientists tune the entanglement structure in an array of qubits

Unveiling the secrets of Montesinho's honey: A blend of tradition and science

Scientists find common genes defending coffee plants against devastating disease

Your morning coffee may be more than a half million years old

Light stands still in a deformed crystal

Some cannabis rolling papers may contain unhealthy levels of heavy metals