Sensing harmful molecules with light

Ultra-sensitive devices are being developed to detect biological and chemical compounds.
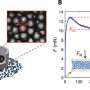
Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) devices are the benchmark in optical sensing. They are used for detecting biomarkers of disease, discovering drugs, analysing chemicals, ensuring food quality and safety, and detecting pollutants in our environment. SPR devices can detect molecules within a few hundred nanometres of their metal surfaces. When a target molecule binds to sensing molecules placed on the device's surface, this alters the path of light travelling through the medium, changing its 'refractive index'. This change is used to indicate the molecule's presence.
Scientists are working on improving the sensitivity, compactness and cost of SPR devices by modifying the materials used to make them.
Brian Corbett and Muhammad Khan of University College Cork in Ireland reviewed the latest research in the field of 'Bloch surface wave' devices, publishing their findings in the journal Science and Technology of Advanced Materials.
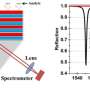
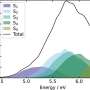
Bloch surface waves (BSW) are light waves that travel on the surface of insulating —or 'dielectric'—materials, such as glass. Researchers are testing the use of dielectric materials, instead of the metals typically used for the surfaces of SPR devices, to develop BSW devices. By doing so, they are detecting even smaller changes in the material's refractive index.
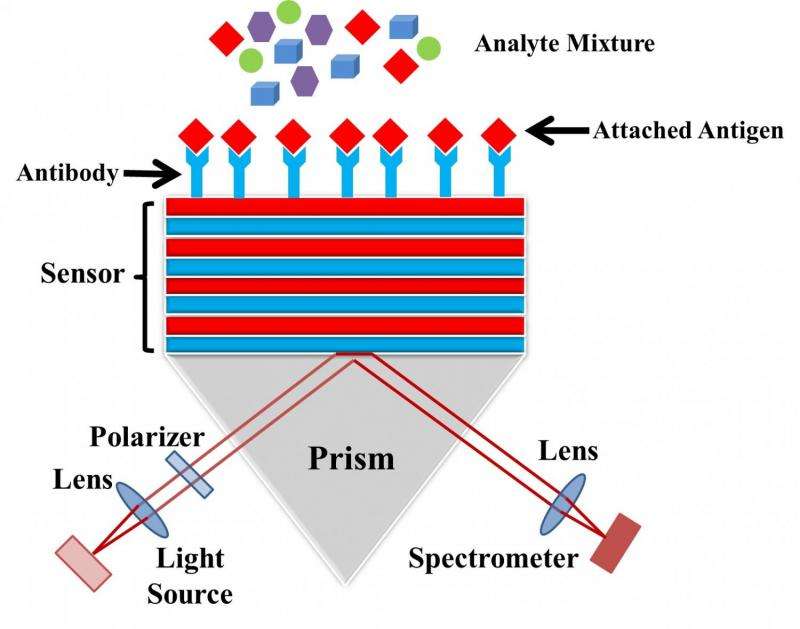
"Bloch surface waves can be used for a variety of sensing applications," says Corbett. "They can also be potentially used as a platform for compact integrated optical circuits," he adds. Corbett expects BSW devices to become commercially available in the coming few years.
Corbett and Khan designed a simple BSW sensor, employing silicon as its surface material, which they believe has practical advantages due to the ease with which it delivers and detects light waves.
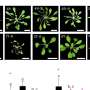
"The research shows that surface waves can be easily generated and they provide a sensitive measure to detect the binding of a material at a surface," says Corbett. "These sensors can provide real-time sensing and may be a way to screen for the presence of biomarkers for different diseases, such as cancer and Alzheimer's disease, at the doctor's surgery."
BSW sensors still need to be tested for their durability in real environments, says Corbett. The team's aim is to develop an on-chip sensing platform with high sensitivity that can ultimately be used in bench top or even smartphone-based devices, he says, with potential application in water quality monitoring.
Journal information: Science and Technology of Advanced Materials
Provided by National Institute for Materials Science