Topological materials for information technology offer lossless transmission of signals
New experiments with magnetically doped topological insulators at BESSY II have revealed possible methods of lossless signal transmission that involve a surprising self-organization phenomenon. In the future, it might be possible to develop materials with such characteristics at room temperature that can be used as processing units in quantum computing, for example. The study has been published in Nature.
New effects in solid-state physics are often first discovered at temperatures near absolute zero (0 Kelvin or -273 °C). Further research can then determine whether and how these phenomena can be induced at room temperature as well. Superconductivity was initially observed in mercury below 4 Kelvin more than 100 years ago. Today, there are many high-temperature superconductors that conduct electrical current without resistive losses at temperatures as high as 138 Kelvin or even 200 Kelvin (the record held by H2S).
The Quantised Anomalous Hall Effect (QAHE) was observed for the first time in a magnetically doped topological insulator below 50 millikelvin in 2013. Similar to superconductivity, this effect allows lossless charge transport within thin edge channels of the samples. Meanwhile, researchers have increased the maximum temperature at which the effect can be observed up to about 1 Kelvin.
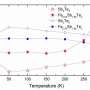
However, based on theoretical considerations, the QAHE should occur at much higher temperatures. So it is a mystery as to why this does not happen. One critical parameter is known as the magnetic energy gap of the sample, it has never been measured it before. The larger this gap, the more stable the effect should be toward the influence of temperature.
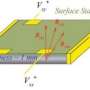
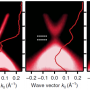
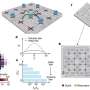
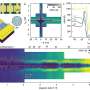
An international team headed by HZB physicist Prof. Dr. Oliver Rader and Prof. Dr. Gunther Springholz from the University of Linz has achieved a breakthrough. Via photoelectron spectroscopy with synchrotron radiation of BESSY II, they have been able to measure the energy gap in such a sample for the first time. To accomplish this, the ARPES1cube was used to reach extremely low temperatures; the researchers used the new spin-resolving capability of the Russian-German Laboratory at BESSY II. Surprisingly, the gap was actually five times larger than theoretically predicted.
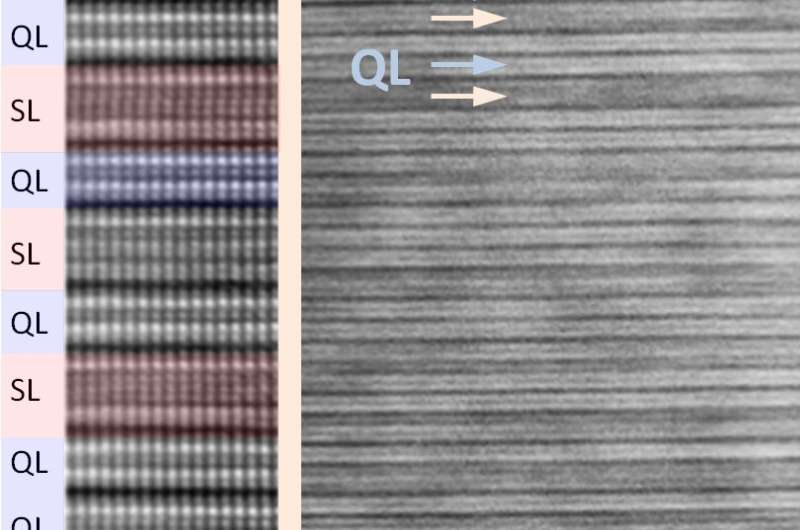
The scientists also found a simple reason for this result: "We now know that manganese doping does not happen in a disordered manner. On the contrary, it causes stratification known as a superstructure in the material—layers much like a puff pastry," explains Springholz. "By adding a few percent of manganese, alternating units of seven and five layers are created. This causes the manganese to be preferentially contained within the seven-layer units and thus can generate the energy gap much more effectively."
Rader says in retrospect that researchers' imaginations in using dopants has not extended far enough to date. They used trivalent elements such as chromium and vanadium that have magnetic characteristics to substitute for the bismuth in bismuth telluride (Bi2Te3), with the dopant atoms in a disordered state. The reason for this seemed very convincing: Trivalent magnetic elements contribute three electrons to chemical bonds and their chemical valence leads these elements to the bismuth sites.
With manganese, the situation is different. Since manganese is bivalent, it does not really fit well in the bismuth sites. That is apparently why the system becomes radically restructured and creates a new double layer of atoms in which manganese can be bivalently incorporated. "In this way, a structure is created in a self-organized way in which manganese can produce the large magnetic energy gap," explains Rader.
If these self-organization phenomena are exploited in specific ways, then completely new configurations can emerge for magnetic topological materials, according to Springholz. In principle, the gap that has now been measured is already so large that it should enable construction of a near-room-temperature QAHE from appropriate components. However, other parameters still need to be improved. A magnetic topological insulator like this in combination with an ordinary superconductor could also permit the realization of a quantum processing unit (Qbit) for a quantum computer.
More information: Large magnetic gap at the Dirac point in Bi2Te3/MnBi2Te4 heterostructures, Nature (2019). DOI: 10.1038/s41586-019-1826-7 , nature.com/articles/s41586-019-1826-7
Journal information: Nature
Provided by Helmholtz Association of German Research Centres